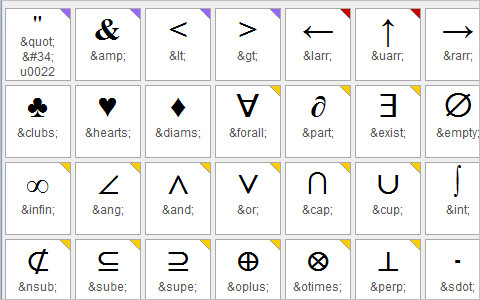
Some characters have a special meaning in HTML, like the less than sign (<) that defines the start of an HTML tag. If we want the browser to actually display these characters we must insert character entities in the HTML source. The following HTML tutorial will go over the various HTML entities available for your use.
A character entity has four parts:
- An ampersand (&),
- An entity name or a #
- An entity number,
- Finally a semicolon (;).
The most common character entity in HTML is the non-breaking space. Normally HTML will truncate spaces in your text. If you write 10 spaces in your text, HTML will remove 9 of them. To add spaces to your text, use the
| Result | Description | Entity Name | Entity Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| non-breaking space | |   | |
| < | less than | < | < |
| > | greater than | > | > |
| & | ampersand | & | & |
| “ | quotation mark | " | " |
| ‘ | apostrophe | ' | |
| Result | Description | Entity Name | Entity Number |
| ¢ | cent | ¢ | ¢ |
| £ | pound | £ | £ |
| ¥ | yen | ¥ | ¥ |
| § | section | § | § |
| © | copyright | © | © |
| ® | registered trademark | ® | ® |
| × | multiplication | × | × |
| ÷ | division | ÷ | ÷ |
So let’s take a look at how we would go about writing this out. Let’s take a very common example, some footer copyright text:
<p>© 2011 My Website ® All Rights Reserved </p>
This will produce the following:
© 2011 My Website ® All Rights Reserved